Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It’s a progressive condition that can lead to serious dental and overall health problems if left untreated. In this article, we’ll explore what gum disease is, its causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Gum Disease
What causes periodontal disease, and how can you avoid it?
Gum disease is primarily caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which is more difficult to remove and can irritate the gums.
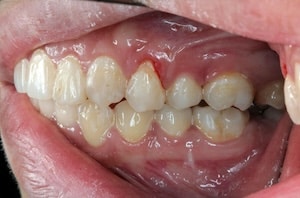
Stages & Types of Gum Disease
There are two primary types or stages of periodontal disease: Gingivitis and Periodontitis.
- Gingivitis: The early stage of gum disease is gingivitis. During this phase, the gums become red, swollen, and may bleed easily. Gingivitis is usually reversible with proper dental hygiene and professional cleaning.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to periodontitis. In this stage, the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. The body’s immune response to the infection, combined with bacterial toxins, starts breaking down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
It’s crucial to recognize the signs of gum disease early. Symptoms of periodontal disease include:
- Gums that bleed during and after tooth brushing
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Persistent bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
- Receding gums
- Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
- Loose or shifting teeth

Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of gum disease. Here are a few of the most common causes of periodontal disease.
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Genetic predisposition
- Certain illnesses, such as diabetes
- Medications that reduce saliva flow
- Hormonal changes, such as those related to pregnancy
- Poor nutrition
Diagnosis and Treatment
Dentists diagnose gum disease based on a dental exam, assessment of symptoms, and measuring the depth of the pockets around teeth. Treatment depends on the stage of the disease and may include:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Professional dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar
- Scaling and root planing to clean below the gum line and smooth the tooth root to help gums reattach
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Flap surgery to remove tartar from deep pockets
- Bone and tissue grafts to regenerate any bone or gum tissue lost to periodontitis
Prevention of Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease involves maintaining good oral hygiene. This includes:
- Brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Regular dental check-ups and cleanings
- Avoiding tobacco products
- Eating a balanced diet for optimal nutrition
Conclusion
Gum disease is a prevalent and potentially serious condition. However, with proper care and early intervention, it is preventable and manageable. Regular dental visits, good oral hygiene practices, and lifestyle changes are key to preventing and treating gum disease.
For more information on gum disease, its treatment, and prevention, contact us today!
